Types of Solar Panels: Present and Future of Costs and Efficiencies
Mitsui Chemicals India Blog Series
2022.08.01
Mitsui Chemicals India Pvt. Ltd.
Energy consumption in India is projected to double by 2050, with vast solar power potential. Given the enormous capacity, the solar resource still has an untapped fraction beyond its present usage.
On account of several technological advancements, the industry is augmented to utilize cost-effective opportunities for different types of solar panels. With its exceeding significance in India, firms are committed to driving innovation and scale to deliver highly efficient solar cells.
Photovoltaics are composed of semiconducting materials, which vary in characteristics and performance attributes. Thus, the efficiency of a solar panel is directly proportional to the intrinsic properties of the semiconductor used.
Read on to find more about the different types of solar panels, their costs, challenges, and overall scope in the future.
What are the Different Types of Solar Panels?
Solar module manufacturing in India is continually improving with newer materials to harness the complete spectrum of solar radiation. In theory, for energy sources to operate, solar cells are manufactured to convert light energy to electricity forming photovoltaic cells. A number of these cells are positioned within semiconducting materials to transfer electricity thence produced.
While the most commonly used material in a solar power plant is Silicon, some of them have an advanced composition. The amount of energy harnessed emitted by PV modules varies in costs, installations, impressions, etc. Such advances have categorized photovoltaics into three major types— Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-film.
It is crucial to choose the best-suited module as per the desired characteristics and attributes. Listed below are some of the most popular solar panels in India.
1. Monocrystalline Solar PV Module Cell:
Mono i.e. single-crystalline solar module is manufactured using silicon crystal. Cylindrical silicon ingots are sliced into thin silicon wafers, which are finally assembled in the form of a rectangle, and framed to manufacture solar cells.
The manufacturing process involves the use of a single piece of silicon, thus the flow of electrons is comparatively more. This is why it is most commonly and effectively used to harness solar energy. Higher PV efficiency thereby helps in reducing the overall electricity cost and makes it a viable option for long-term effectiveness.
In terms of appearance, Monocrystalline solar modules are typically black with black, silver, or white metal frames.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Cell:
Similar to monocrystalline solar modules, polycrystalline solar cells are composed of silicon as well. Although the manufacturing process does not involve the use of a single piece, rather multiple fragments of silicon are melted together.
Since the composition of silicon varies in both the solar panels, raw fragments of silicon result in relatively less space for electrons to flow. Polycrystalline modules have turned out to be more cost-friendly because they tend to have lower wattages. Here’s what makes the difference, and the resilience specific to the installation prospects.
Unlike single-crystalline panels, polycrystalline cells tend to have blue colored hue due to the blend of several raw layers of silicon.
3. Thin-film Solar Cell:
As the name suggests, thin-film modules are significantly thinner than crystalline wafers. Generally composed of semiconducting materials such as amorphous silicon, each of these areas is deposited over the glass/films to develop a solar cell. In India, thin-film solar panels are mostly manufactured from Cadmium Telluride (CdTe).
Despite their low-efficiency ratings, thin films are widely used in large-scale projects and industrial installations. In the most primitive sense, these solar modules are widespread that are not suitable for residential purposes. However, thin-film photovoltaics serve in various flexible applications to meet your energy needs.
Using different semiconductors such as CdTe and amorphous silicon, thin-film solar cell comes in both blue and black colored hue.

The solar industry is continuously undergoing innovation. Through such developments, manufacturers are committed to maximizing PV module efficiency and manufacturing easy-to-manage panels. With competitive advantages, the sector has observed a dramatic cost-cut.
Silicon, being the prime raw material for manufacturing a solar module, is almost inexpensive. This, in turn, provides an edge to decrease the costs further and offer a higher rate on investments.
How Effective is Your Solar Panel: A Comparative Analysis
Apart from the manufacturing processes and appearance, factors that are considered while making a choice include− Efficiency, Affordability, and Temperature. Let us divide the three major types of solar panels into these two categories.
1. Efficiency:
Efficiency measures the amount of power produced coinciding with the consumed solar radiation. Broadly, crystalline panels offer higher efficiency than thin-film panels, with monocrystalline panels acceding the other two. The differentiating factor is the utilization of a single, pure cut of silicon which allows free conduct of electricity through it.
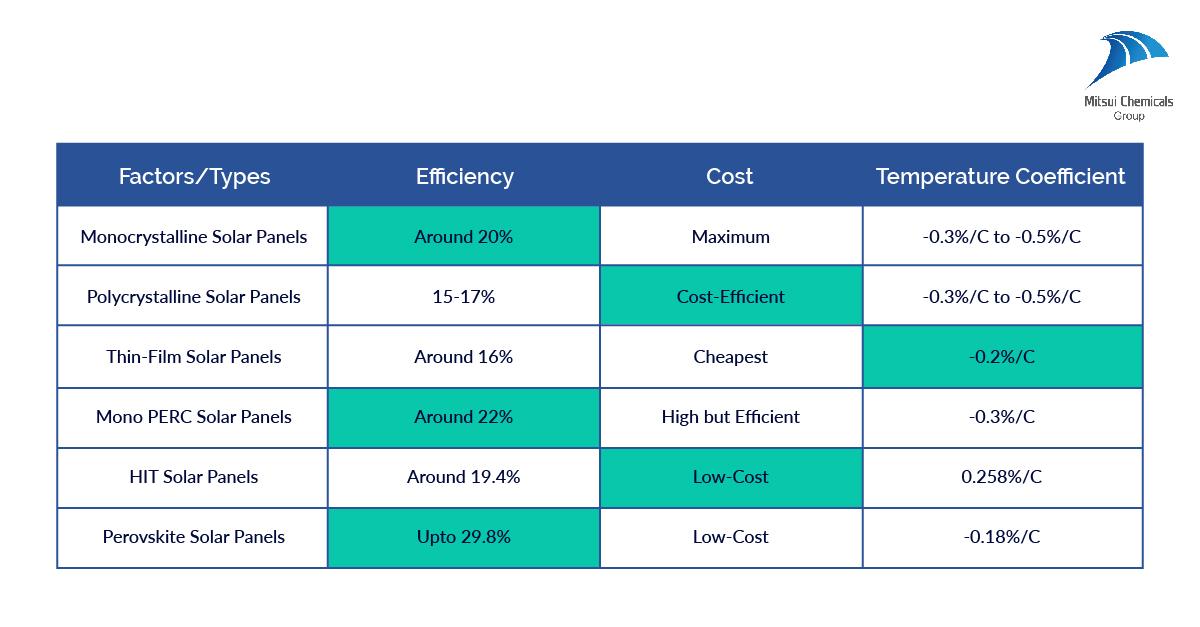
Most monocrystalline solar cells have around 20% efficiency. Followed by Polycrystalline panels with around 15-17% efficacy, and finally, thin film that reaches up to 16%.
With greater power output, monocrystalline panels are ideal for homes with confined spaces. Even the smallest of panels have the capability to produce much more efficiently than thin-film solar cells.
There is a tremendous scope for improvement when polycrystalline panel efficiency ratings are considered. With new technological improvements, manufacturers can easily bridge this gap.
Lastly, thin-film modules produce the lowest electric output and are used more in number when compared to crystalline modules. Hence, they are best suited for open spaces i.e. commercial buildings with large rooftops.
2. Cost:
Designing a solar module that is both cost-friendly and efficient is challenging but possible. The key to achieving this would be targeting the performance and driving the ultimate potential of silicon because it’s cheap. Polycrystalline solar modules are the most cost-effective of all three.
The question that arises- Even after higher efficiency ratings of Monocrystalline panels, why is it not a viable option in terms of cost? Simply, the manufacturing process of the two crystalline modules varies with their raw materials.
Although, the major raw material used is Silicon, for single-crystalline-the pure form is used, while fragments of silicon can be used for Polycrystalline.
Monocrystalline module manufacturing involves crystal formation, which results in a higher cost and even wastage to some extent. Likewise, a relatively simpler process in the production of polycrystalline modules makes them cost-efficient. Thin-film solar panels are usually the cheapest since they require less equipment and space. However, they require maintenance frequently and thereby do not retain the cost-effectiveness in the long run.
3. Temperature Coefficient:
The most important factor of the varied performance is the retention of the temperature. Certain PV modules are capable of amplifying power output with an increase in temperature i.e. high-temperature coefficient.
Both Monocrystalline & Polycrystalline solar cells tend to possess a temperature coefficient of about -0.3%/C to -0.5%/C. While thin-film modules have coefficients of about -0.2%/C. Therefore, the heat handling capacity of thin-film solar panels is considered advantageous.
Besides heat tolerance, thin-film solar cells have the most aesthetic appearance and slim fit that allows them to blend seamlessly. Nonetheless, it is not always common for sleek panels, as they require a large open space probably the whole roof.
In light of renewable sources of energy onboarding to almost everywhere, factors concerning solar panel choice must be taken care of. It is equally important to foresee all the conditions that the PV module will be subjected to.
Best Type of Solar Panel: Bottom Line
India is witnessing an exponential rate of growth in solar panel installations and efficiency whilst reducing the cost at the same time. Perhaps the most crucial thing to making the most of this accelerating growth is− Right Investment.
With careful consideration and ideal conditions in mind, Monocrystalline panels are the most efficient choice, yet the most expensive one. Thin-film cells are the least expensive, yet the least efficient. Moreover, polycrystalline panels are moderately expensive as well as efficient. The only rational option is to decide the purpose and installation space.
In conclusion− The best-suited option for residential purposes with compact accommodation is Monocrystalline solar panels. Additionally, these panels tend to have a higher lifespan and durability which makes them a good household investment.
Given the varied application of Polycrystalline panels, both for small- and large-scale installations, they are perfect for maximizing energy bill savings in a small space.
Commercial roofs that are not capable enough to hold the additional weight of traditional panels make the most of thin-film panels because of their lighter weight and sleek design.
Choosing the Right System with Mitsui Chemicals India
The efficiency of any solar panel installation calls for reliable technical support before and maintenance after. With Mitsui at your service, we deliver advisory services to help you determine the suitable panels for every unique application. Moreover, we ensure risk management at all stages of your PV project, to offer quality assurance from development to final operation.
Abiding by the international standards (IEC) and NABL accredited module testing facility, with our strong quality control, we offer timeless assistance to detect root causes and provide meticulous corrective action. Our team of professional engineers works closely to perform quality inspections and site assessments. This helps in establishing efficient, cost-friendly, and high-performance solar panels to maintain the uptime potential of your business operations.
Solar panel installation is a long-term investment only if it has been managed that way. At Mitsui, we have envisioned a bright future for the solar industry.
If you seek reliable installing, operating, and maintenance services for a seamless solar power experience, contact us.
